무한 스크롤은 offset이 아니라 마지막으로 읽은 데이터의 id를 기억해서 스크롤을 내리면 그 지점부터 로딩하는 방식으로 동작한다.
왜 이렇게 하냐면, offset방식으로 했다가는 중간에 데이터가 삭제되거나 추가되었을 때 조회가 누락되거나 중복되기 때문이다.
보통 페이지네이션 방식은 커뮤니티 사이트들이 쓰고, 무한 스크롤 방식은 SNS에서 쓴다.
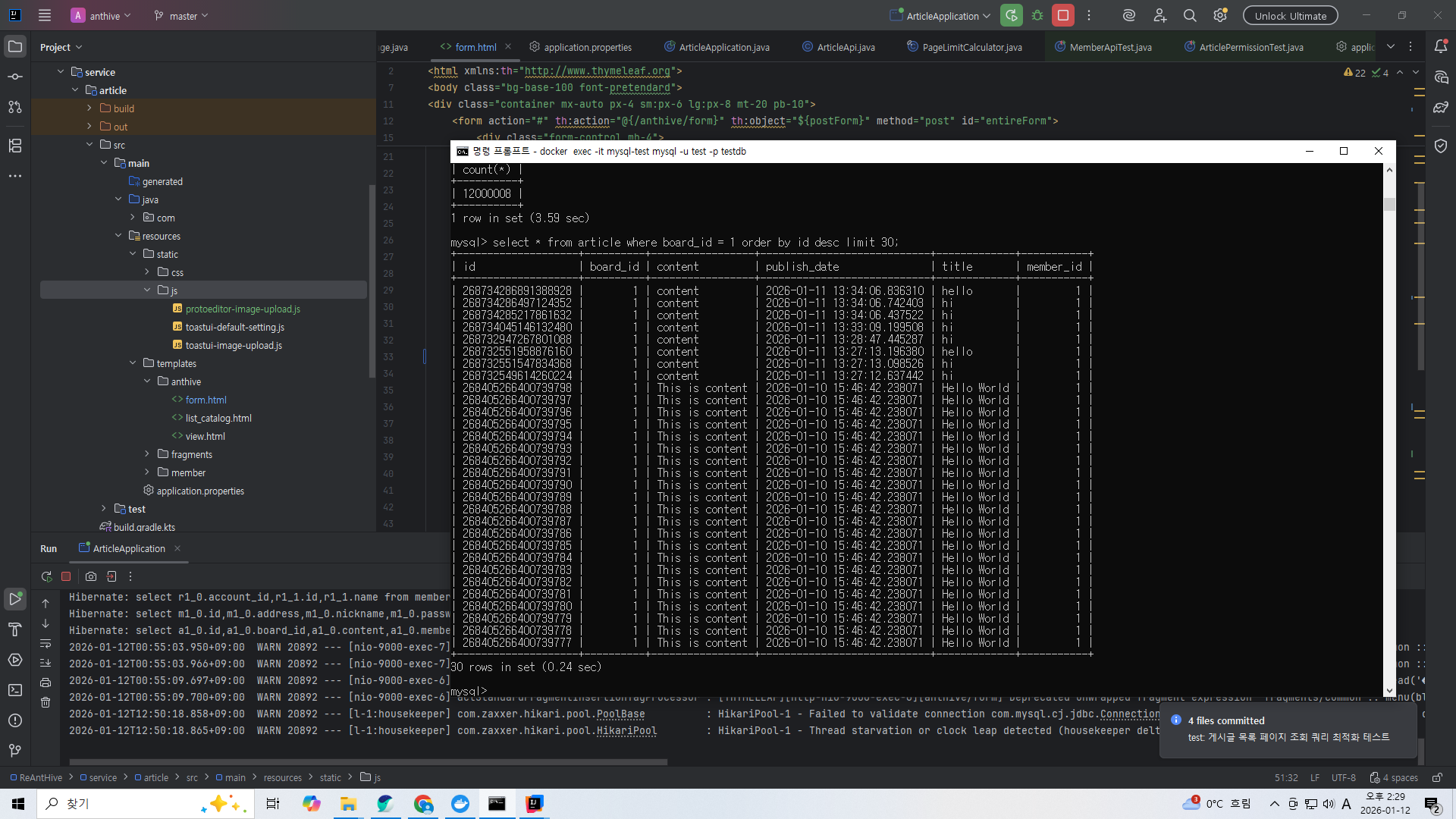
select * from article where board_id = 1 order by id desc limit 30;
이미 인덱스가 id기준 내림차순 정렬이 되어 있으므로 내림차순으로 처음 30개를 조회하면 빠르게 조회된다.
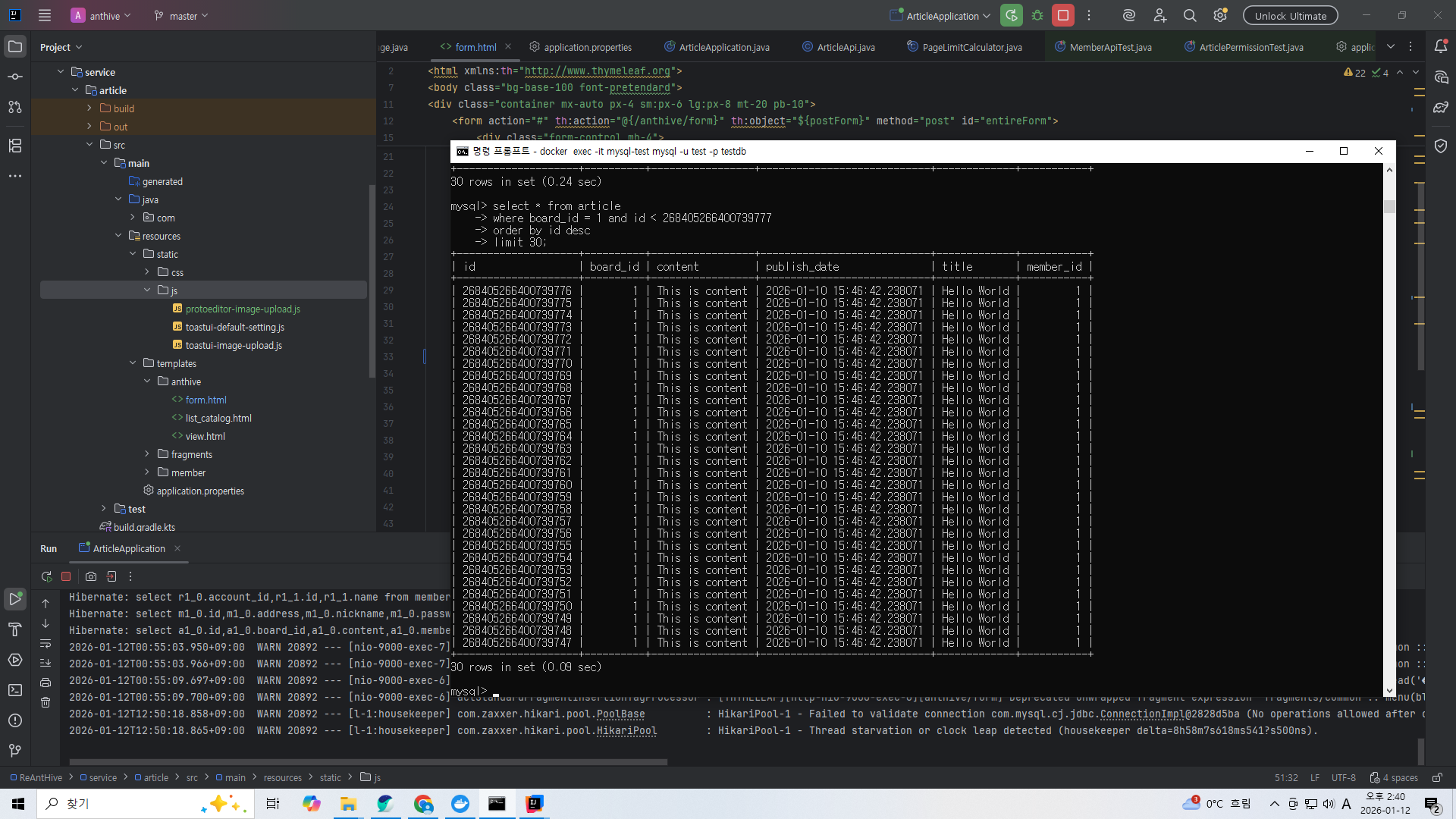
select * from article where board_id = 1 and id < 268405266400739777 order by id desc limit 30;
그 다음 30개를 조회해보자.
30번째 id보다 작은 id부터(내림차순이니까) 조회하면 된다.
마지막 id를 지정하기만 하면 언제나 일정한 속도로 조회가 가능하다.
@Query(
value = "select article.id, article.title, article.content, article.board_id, article.member_id, " +
"article.publish_date " +
"from article " +
"where board_id = :boardId " +
"order by id desc limit :limit",
nativeQuery = true
)
List<Article> findAllInfiniteScroll(@Param("boardId") Long boardId, @Param("limit") Long limit);
@Query(
value = "select article.id, article.title, article.content, article.board_id, article.member_id, " +
"article.publish_date " +
"from article " +
"where board_id = :boardId and id < :lastArticleId " +
"order by id desc limit :limit",
nativeQuery = true
)
List<Article> findAllInfiniteScroll(
@Param("boardId") Long boardId,
@Param("limit") Long limit,
@Param("lastArticleId") Long lastArticleId
);이제 리포지토리에 방금 쿼리 2개 넣었던 것처럼 두개의 쿼리 함수를 만들어 주면된다.
첫 limit개 조회 쿼리와 마지막 조회 지점부터 limit개 조회 쿼리.
@Test
void findInfiniteScrollTest() {
List<Article> articles = articleRepository.findAllInfiniteScroll(1L, 30L);
for (Article article : articles) {
log.info("articleId = {}", article.getArticleId());
}
Long lastArticleId = articles.getLast().getArticleId();
List<Article> articles2 = articleRepository.findAllInfiniteScroll(1L, 30L, lastArticleId);
for (Article article : articles2) {
log.info("articleId = {}", article.getArticleId());
}
}이건 테스트 코드
public List<ArticleResponse> readAllInfiniteScroll(Long boardId, Long pageSize, Long lastArticleId) {
List<Article> articles = lastArticleId == null ?
articleRepository.findAllInfiniteScroll(boardId, pageSize) :
articleRepository.findAllInfiniteScroll(boardId, pageSize, lastArticleId);
return articles.stream().map(ArticleResponse::from).toList();
}서비스.
@GetMapping("/v1/articles/infinite-scroll")
public List<ArticleResponse> readAllInfiniteScroll(
@RequestParam("boardId") Long boardId,
@RequestParam("pageSize") Long pageSize,
@RequestParam(value = "lastArticleId", required = false) Long lastArticleId
) {
return articleService.readAllInfiniteScroll(boardId, pageSize, lastArticleId);
}컨트롤러.
패러미터로 마지막으로 읽은 지점을 보내주는건 프론트엔드단에서 알아서 하겠지.
@Test
void readAllInfiniteScrollTest() {
List<ArticleResponse> articles1 = restClient.get()
.uri("/v1/articles/infinite-scroll?boardId=1&pageSize=5")
.retrieve()
.body(new ParameterizedTypeReference<List<ArticleResponse>>() {
});
System.out.println("firstPage");
for (ArticleResponse articleResponse : articles1) {
System.out.println("articleResponse.getArticleId() = " + articleResponse.getArticleId());
}
Long lastArticleId = articles1.getLast().getArticleId();
List<ArticleResponse> articles2 = restClient.get()
.uri("/v1/articles/infinite-scroll?boardId=1&pageSize=5&lastArticleId=%s".formatted(lastArticleId))
.retrieve()
.body(new ParameterizedTypeReference<List<ArticleResponse>>() {
});
System.out.println("secondPage");
for (ArticleResponse articleResponse : articles2) {
System.out.println("articleResponse.getArticleId() = " + articleResponse.getArticleId());
}
}테스트 코드
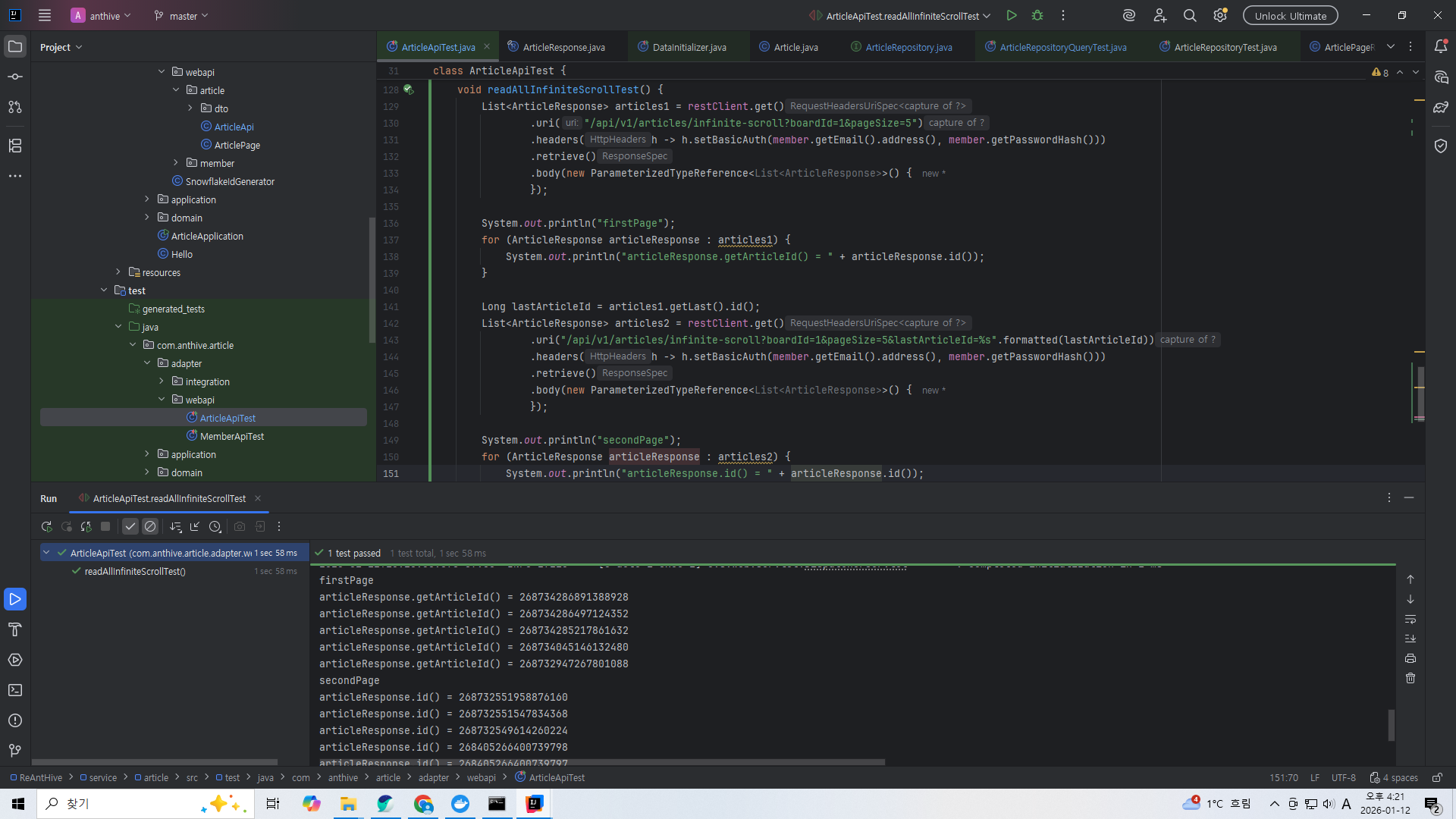
잘 동작한다.
'스프링 부트로 블로그 서비스 개발하기' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 댓글 기능 - 댓글 엔티티, 리포지토리, 서비스, 컨트롤러 (0) | 2026.01.16 |
|---|---|
| 댓글 기능 - 새 모듈 만들고 설정 (0) | 2026.01.13 |
| 포스트 CRUD 기능 - 커버링 인덱스 방식으로 게시글 목록의 페이지 조회 쿼리 최적화 (0) | 2026.01.11 |
| 포스트 CRUD 기능 - 인덱스 생성 및 커버링 인덱스 (1) | 2026.01.11 |
| 포스트 CRUD 기능 - 쓰레드풀을 써서 게시글 대량 삽입 테스트 (0) | 2026.01.10 |